This is where the magic MATH happens ✨
All the tools of choreography work together to shape the expression we outlined with the Eight Efforts. In practice, easing is the expressive core of the motion parameters. The easing function you choose profoundly influences how duration, delay, direction, repetition, and origin feel.
What is an easing function?
An easing function is a mathematical function that maps normalized time to normalized progress, shaping speed and acceleration across a set duration.
Put simply: it tells you how motion unfolds over time.
- Duration: total time T
- Distance: total change D
- Easing: E(u) where u = t / T and E returns a value in [0, 1]
// Position over time with easing
const position = (t, { origin, distance, duration, easing }) => origin + distance * easing(t / duration)
FINE. Let’s simplify.
In CSS and JS we often see easing represented as either a linear function or a bezier-curve function.
Let’s talk about bezier-curves first.
Bezier Curves
A bezier curve, when applied to motion, is a mathematical function that maps normalized time to normalized progress, shaping speed and acceleration across a set duration.
Put simply: it tells you how motion unfolds over time.
When a bezier curve has a single control point it’s called a quadratic curve.
When it has two control points it’s called a cubic curve. These are the most common types of bezier curves used in motion design.
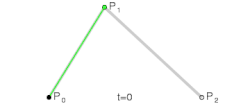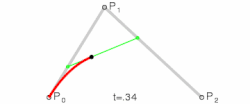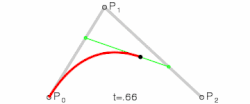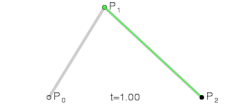
Bezier curves are a beautiful abstraction for describing curves. The most commonly used form, cubic bezier curves, reduce the problem of describing and storing a curve down to storing 4 coordinates. — Jamie Wong
Linear Function
The linear function is a fairly new CSS function (full support JUST happened in 2023) that provides a simple way to create linear easing.
